Page 1
ReponsePage 2
ReponsePage 3
Question WBBPage 4
Reponse ComPage 5
Question StPage 6
Reponse OLPage 7
Question WTSPage 8
Reponse ELBPage 9
Question ConPage 10
Reponse NSPage 11
QuestionPage 12
Reponse NSPage 13
QuestionPage 14
Reponse BrPage 15
Reponse SpPage 16
Reponse PNPage 17
Question WMPage 18
Reponse NvPage 19
Reponse glPage 20
Question TyPage 21
Reponse SePage 22
Reponse MoPage 23
Reponse InPage 24
Question StrPage 25
Reponse ClPage 26
Reponse BuPage 27
Question NeuPage 28
Reponse CePage 29
Reponse PrPage 30
QuestionPage 31
Reponse denPage 32
Reponse AxPage 33
QuestionPage 34
QuestionPage 35
Reponse SyPage 36
Question fuPage 37
Reponse RePage 38
Reponse HwPage 39
Question InPage 40
Reponse CHPage 41
Reponse BSPage 42
QuestionPage 43
Reponse hbPage 44
Reponse mbPage 45
Reponse bbPage 46
QuestionPage 47
Reponse rofPage 48
Question HOPage 49
Reponse ChPage 50
QuestionPage 51
Reponse thPage 52
Reponse htPage 53
QuestionPage 54
Reponse coPage 55
Reponse ccPage 56
Question KFPage 57
Reponse VolPage 58
Reponse RWPage 59
QuestionPage 60
Reponse LRPage 61
Reponse NAPPage 62
Question HWPage 63
Reponse CopPage 64
Reponse ComPage 65
Reponse MAPage 66
Reponse ChePage 67
Reponse DesPage 68
Reponse AxPage 69
Reponse MAPage 70
Question KN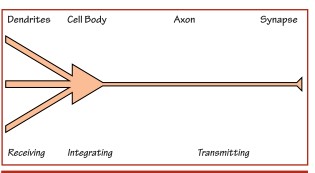
Page 71
Reponse DenPage 72
Reponse BodPage 73
Reponse AxPage 74
Reponse SynPage 75
Reponse RePage 76
Reponse IntPage 77
Reponse TrPage 78
Question FoPage 79
Reponse Sp
Page 80
Reponse Pyr
Page 81
Reponse Pur
Page 82
Question PaPage 83
Reponse MemPage 84
Reponse CytPage 85
Reponse ComPage 86
Reponse DSPage 87
Question DesPage 88
Reponse GFPage 89
Reponse DynPage 90
Reponse SynPage 91
Question Do?Page 92
Reponse ExPage 93
Reponse InPage 94
Reponse TrgPage 95
Reponse AxPage 96
Question Do?Page 97
Reponse APPage 98
Reponse NaPage 99
Reponse KPage 100
Reponse STPage 101
Reponse IPPage 102
Reponse APPage 103
Question ElsPage 104
Reponse InPage 105
Reponse GapPage 106
Question LikPage 107
Reponse DigPage 108
Reponse FeqPage 109
Reponse ChMPage 110
Question WAPage 111
Reponse SVPage 112
Reponse ACEPage 113
Question WPPage 114
Reponse APPage 115
Reponse CaPage 116
Reponse EZPage 117
Question TyPage 118
Reponse SnPage 119
Reponse TaPage 120
Reponse BrPage 121
Reponse VFBPage 122
Reponse SCPage 123
Question AfPage 124
Reponse VRPage 125
Question AfPage 126
Reponse TrPage 127
Reponse RePage 128
Reponse RcPage 129
Reponse L&KPage 130
Reponse +FPage 131
Reponse epPage 132
Reponse ThPage 133
Question WTPage 134
Reponse ExPage 135
Reponse InPage 136
Question WtPage 137
Reponse GBPage 138
Reponse GlyPage 139
Question HWPage 140
Reponse T&T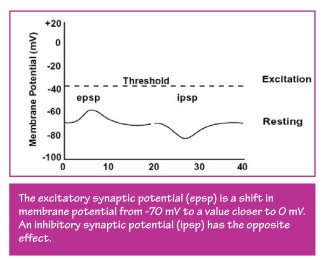
Page 141
Question DGAPage 142
Reponse D&BPage 143
Reponse T&PPage 144
Reponse VisPage 145
Reponse MovPage 146
Reponse DevPage 147
Reponse DysPage 148
Reponse PlaPage 149
Reponse L&MPage 150
Reponse StrPage 151
Reponse ImSPage 152
Reponse SlpPage 153
Reponse BImPage 154
Reponse ArtPage 155
Reponse WroPage 156
Reponse EthPage 157
Reponse T&C